
Edublox aims to help children read, learn, and achieve at a cognitive and academic level.
Cognitive skills are intellectual skills used in acquiring knowledge, manipulating information, reasoning, and problem-solving. Cognitive skills include attention; visual and auditory processing and processing speed; several types of memory, and logical thinking. Academic skills include reading, spelling, reading comprehension, and math.
Our websites contain 800+ documented successes of students whose lives were changed through our integrative approach, the latest addition being three 2024 peer-reviewed publications that show significant improvements in reading, literal comprehension, and spelling.
Improved reading, comprehension, spelling
An Edublox program significantly improved the word recognition of students with reading difficulties over a period of 8 weeks (21 hours). Word recognition is the ability to recognize words at a glance. The Edublox group’s mean (n = 14) improved from 5.64 to 18.50, while the control group improved from 4.69 to 9.00 (n = 13). The maximum score is 20. The post-test mean difference between the two groups is 9.50 (Jatau et al., 2024, Journal of Human, Social and Political Science Research).
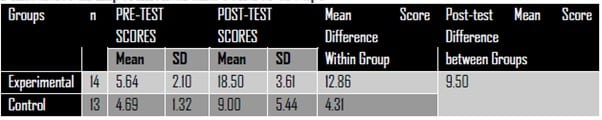
This means the Edublox group improved from 28% to 93%, and the control group from 23% to 45% on the word recognition test.
The Edublox program also significantly improved the literal comprehension of these students. The Edublox group’s mean improved from 1.57 to 18.14, while the control group improved from 1.54 to 2.42. The maximum score is 20. The post-test mean difference between the two groups is 15.72 (Jatau et al., 2024, Journal of Education Research and Library Practice).
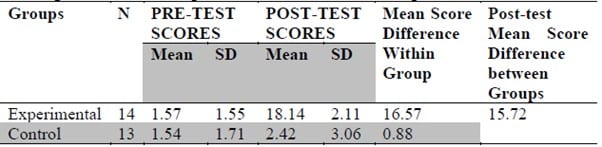
This means the Edublox group improved from 8% to 91%, and the control group from 8% to 12% on the comprehension test.
The Edublox program significantly improved the spelling ability of these students as well. The Edublox group’s mean improved from 4.14 to 19.07, while the control group improved from 3.38 to 7.25. The maximum score is 20. The post-test mean difference between the two groups is 11.82 (Jatau et al., 2024, Sapientia Foundation Journal of Education, Sciences and Gender Studies).
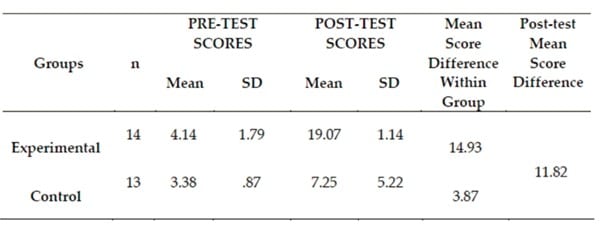
This means the Edublox group improved from 21% to 95%, and the control group from 17% to 36% on the spelling test.
Improved cognitive skills
Our other 800+ documented successes include research from Singapore with 27 Grade 6 students and a matching control group. The CEA in the Faculty of Education at the University of Pretoria analyzed the results, showing a statistically significant improvement in focused attention over five days (18 hours of training). Over and above, the effect size is large.
The experimental group in a study by Dr. Mays (2014, University of Johannesburg) showed an improvement of 1.3 years in visual memory and 1.5 years in visual sequential memory after receiving intensive Edublox training over five days (22.5 hours of training).
Dr. Lee deLorge in Ohio tested 67 students aged 5 to 18 with ADHD, dyslexia, dyscalculia, and non-specific learning disabilities. The processing speed of 94% of the learners improved significantly:
- 35 ADHD students: 52.45% combined increase (37.24% pre-test avg/89.69% post-test avg);
- 13 dyslexic students: 46.76% combined increase (41.31% pre-test avg/88.07% post-test avg);
- 2 students with dyscalculia: 57.38% combined increase (39.76% pre-test avg/97.14% post-test avg);
- The remaining students were non-specific LD: 64.14% combined increase (30.40% pre-test avg/94.54% post-test avg).
A study by Dawood at UP confirmed that exposure to the Edublox program significantly improves processing speed. Sixty-four 2nd-grade students were divided randomly into three groups: group 1 completed 28 hours of Edublox’s computer-based cognitive program for three weeks; group 2 was exposed to computer games, while group 3 continued with their schoolwork.
A study by De Wet found an increase in nonverbal IQ scores of 11.625 in deaf children after 27.5 hours of Edublox instruction, which was confirmed by our own trials of hearing children: an increase of 5.6 in verbal IQ and 12.5 in nonverbal IQ after 40 hours of instruction.
