Developed in 1983 by developmental psychologist Howard Gardner, schools and educators worldwide have embraced the use of his multiple intelligences test. Gardner’s theory of multiple intelligences considers cognitive capabilities using a wide range of scope instead of a singular standardized test.
Unlike a traditional test of intelligence, this multi-faceted approach believes that children learn in several ways.
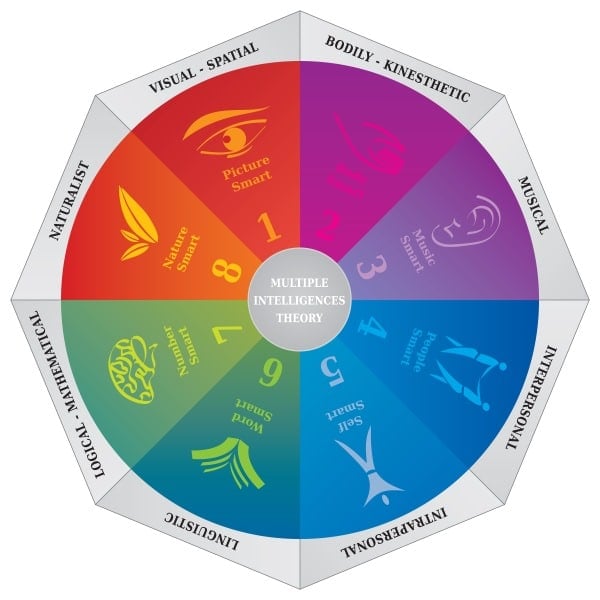
His book, Frames of Mind, covers what Gardner considers the eight intelligences used in learning:
1. Logical-mathematical
The natural ability to think scientifically and logically and perform complicated mathematical equations, reasoning, and pattern recognition fall under logical or mathematical intelligence. Chess players, scientists, and computer program developers perform very well in this intelligence category.
2. Linguistic
These skills involve verbal and written talent and the ability to memorize vocabulary and dates. Higher linguistic skills are found in authors, translators, and people involved in the media.
3. Visual-spatial
Visualization, perception of the world, and artistic creative ability dictate this area. Increased spatial intelligence is seen in artists, inventors, designers, and architects.
4. Bodily-kinesthetic
This category includes intelligence of a physical nature, such as hand-eye coordination, athletics, and the skill to build things. Attention to detail and muscle control create actors, chefs, and athletes.
5. Musical
Those with a highly developed sense of rhythm, pitch, tone, and even language skills, such as composers, entertainers, and musicians, fall into this category..
6. Intrapersonal
Being capable of reflecting upon one’s own emotions and reactions and viewing one’s personality clearly is part of intrapersonal intelligence. Counselors and philosophers are commonly found to be strong in this area.
7. Interpersonal
Understanding the emotions of others and their relationships is an elemental skill in this area. According to Gardner, therapists, teachers, and clergy tend to test higher in this intelligence region.
8. Naturalist
This is the inane ability to distinguish and perceive the natural world, such as plants and animals. People with these tendencies gravitate toward professions such as gardening, veterinarians, and other areas to work with nature and animals.
The combination of these eight intelligences determines the learning ability of each one of us. Understanding and utilizing these differences to the student’s best advantage can help accelerate learning. Gardner’s theory concludes that while basic linguistic and logical testing is important, they do not determine a person’s ability to assimilate new knowledge.
Gardner’s theory has come under criticism from both psychologists and educators. They argue that his definition of intelligence is too broad and that his eight different “intelligences” represent talents, personality traits, and abilities. Gardner’s theory also suffers from a lack of supporting empirical research.
Despite this, the theory of multiple intelligences continues to be popular with educators.
Edublox offers cognitive training and live online tutoring to students with dyslexia, dysgraphia, dyscalculia, and other learning disabilities. Our students are in the United States, Canada, Australia, and elsewhere. Book a free consultation to discuss your child’s learning needs.

