
In everyday language, the terms length, height, and breadth (or width) are often used interchangeably, but in technical and scientific contexts, they have different meanings and applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for precise communication, particularly in fields such as geometry, engineering, construction, and design.
This article aims to clarify the distinctions between these dimensions and provide examples of their practical applications.
Length
Definition:
Length is the measurement of an object or space from end to end. It is the longest dimension of an object, typically measured in units such as meters, centimeters, inches, or feet.
Application:
- In everyday scenarios, length is commonly used to describe the size of objects such as a piece of fabric, a table, or a road.
- In geometry, length is used to measure the sides of polygons or the distance between two points.
- In physics, length can describe distances traveled by objects or the wavelength of electromagnetic waves.
Example:
- The length of a rectangular table may be 2 meters.
- The length of a room may be 5 meters from one wall to the opposite wall.
Height
Definition:
Height refers to the measurement of an object from its base to its top. It is the vertical dimension, indicating how tall an object or structure is.
Application:
- Height is often used in architecture and construction to describe the size of buildings, towers, and other structures.
- In daily life, height can refer to the size of a person, a tree, or a stack of books.
- In sports, height is used to measure the elevation an athlete reaches, such as in high jump or pole vaulting.
Example:
- The height of a person may be 1.75 meters.
- The height of a skyscraper may be 200 meters from the ground to the top of the building.
Breadth (width)
Definition:
Breadth, also known as width, is the measurement of an object from side to side. It is the dimension that measures how wide an object is.
Application:
- Breadth is used to describe the width of various objects, such as a room, a car, or a piece of paper.
- In design and manufacturing, breadth is critical for ensuring that parts fit together correctly.
- In fashion, the breadth of a garment can determine its fit and comfort.
Example:
- The breadth of a door may be 0.8 meters.
- The breadth of a swimming pool may be 10 meters.
Comparing length, height, and breadth
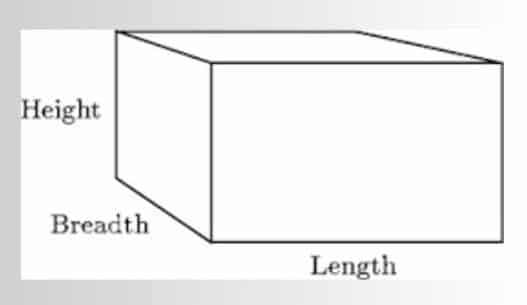
To illustrate the differences more clearly, consider a rectangular box. The box has three dimensions: length, height, and breadth. If we place the box on a flat surface:
- Length is the longest side of the box lying on the surface.
- Height is the vertical dimension from the surface to the top of the box.
- Breadth (width) is the shorter side of the box lying on the surface, perpendicular to the length.
These measurements help define the shape and size of the box in a three-dimensional space.
Practical implications
Understanding the differences between length, height, and breadth is essential in various professional and practical contexts:
- Engineering and construction: Precise measurements ensure that structures are built accurately and safely.
- Product design: Knowing the dimensions of products ensures they fit within specified spaces and meet user requirements.
- Shipping and packaging: Correctly measuring the dimensions of packages ensures efficient use of space and compliance with shipping regulations.
Conclusion
In summary, length, height, and breadth are fundamental dimensions used to describe the size and shape of objects. Length is the longest measurement, height is the vertical measurement, and breadth is the width. Recognizing the differences between these terms is crucial for clear and accurate communication in many fields. Whether you’re designing a building, creating a product, or simply measuring furniture, understanding these dimensions will help you achieve your goals with precision.
Edublox offers cognitive training and live online tutoring to students with dyslexia, dysgraphia, dyscalculia, and other learning disabilities. Our students are in the United States, Canada, Australia, and elsewhere. Book a free consultation to discuss your child’s learning needs.
Authored by Shanice Jordaan. Shanice holds a bachelor’s degree in education and has extensive teaching experience, having taught math for five years and English for three. She leverages her skills as an English teacher, online ESL teacher, and math and reading tutor to design engaging lessons, foster positive learning environments, and cater to diverse learning needs.
